01 Insights & forecasts
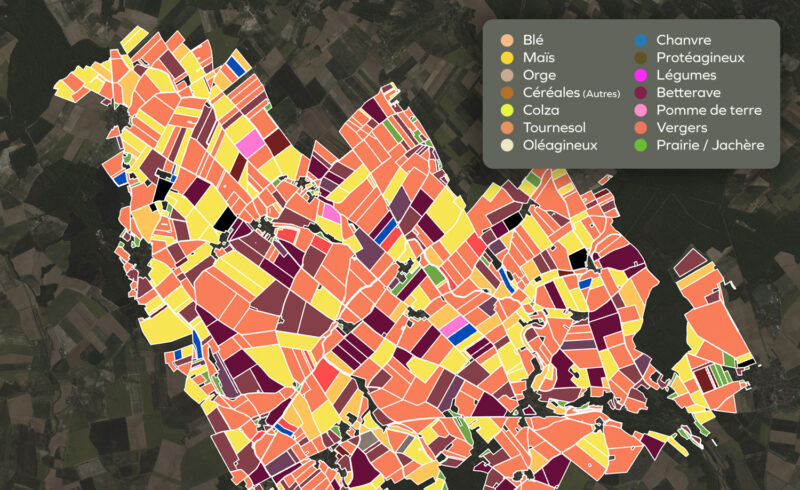
Satellite imagery for crop identification
Unique knowledge on crop rotations, on every field, anywhere in en Europe thanks to non-stop IA-driven satellite imagery analysis by Kermap.
Field boundaries
Available all over Europe (minimum size : 0.5 ha)
Dominant crop type identification
30 classes in France, including winter/summer varieties, and 22 classes in other European countries
Production areas
End-of-season and in-season estimation
Yield estimates
Field crops, end-of-season
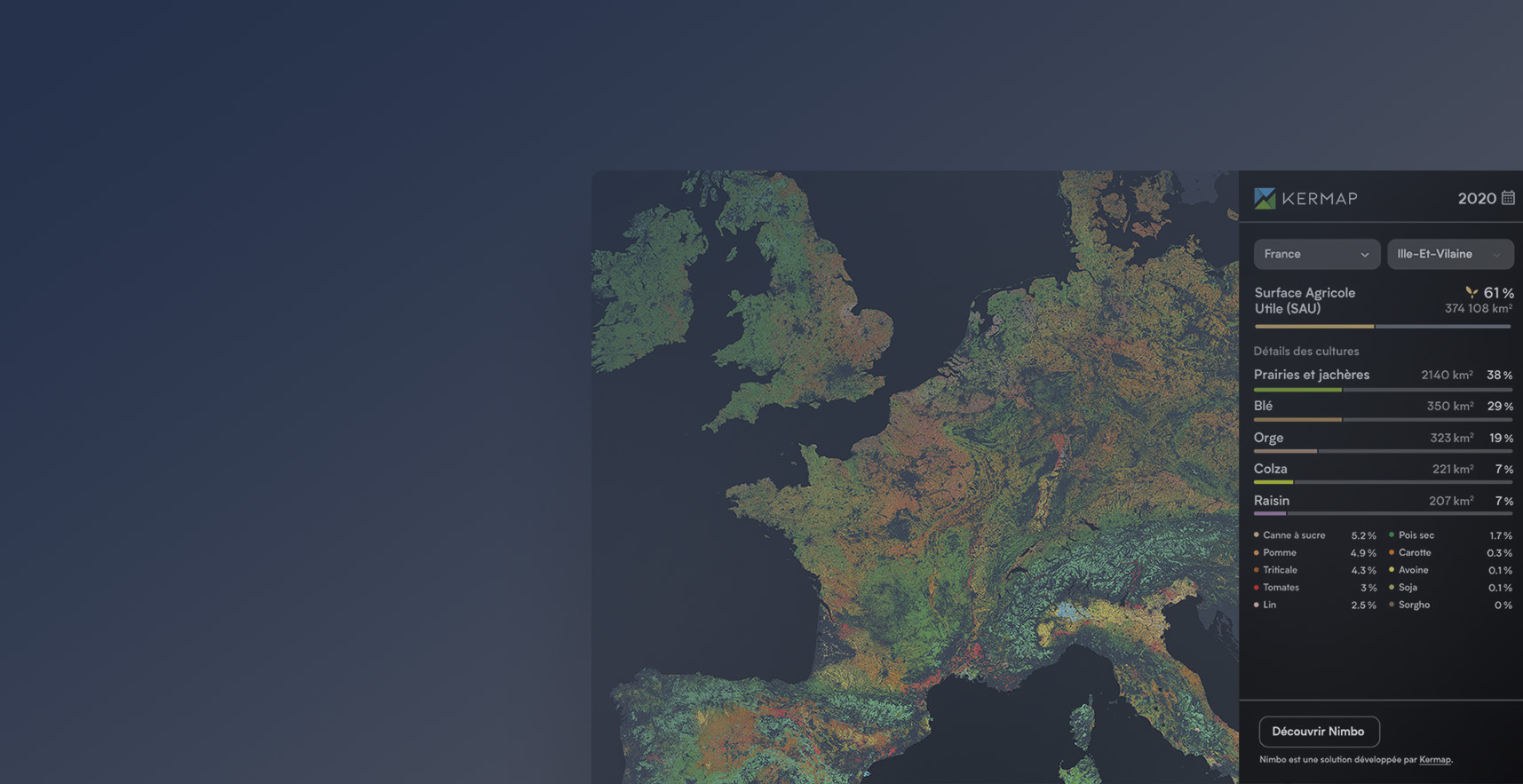

A unique look at European agriculture
Crop inventory over all of Europe’s farming fields, in maps and stats
02 Measure & Verification
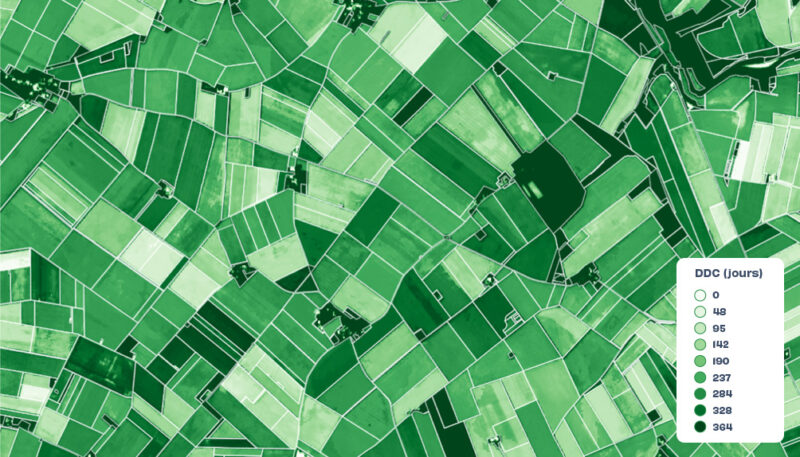

Regenerative agriculture: measuring soil cover
Objective, reliable indicators to quantifiy and validate agroecological transition programs based on soil conservation agriculture
Soil cover duration
In number of days, field by field
Soil cover rate
Identification of intra-field heterogeneity
Cover crop monitoring
Cover crop typology and cover duration
Cover crop biomass
Estimation and modelization of carbon stocked by vegetation

Étude de cas
Saint Louis Sucre – Regenerative agriculture
- Non-stop satellite monitoring from Sentinel imagery
- Automatic identification of covered/non-covered fields
- Calculation of annual soil cover duration
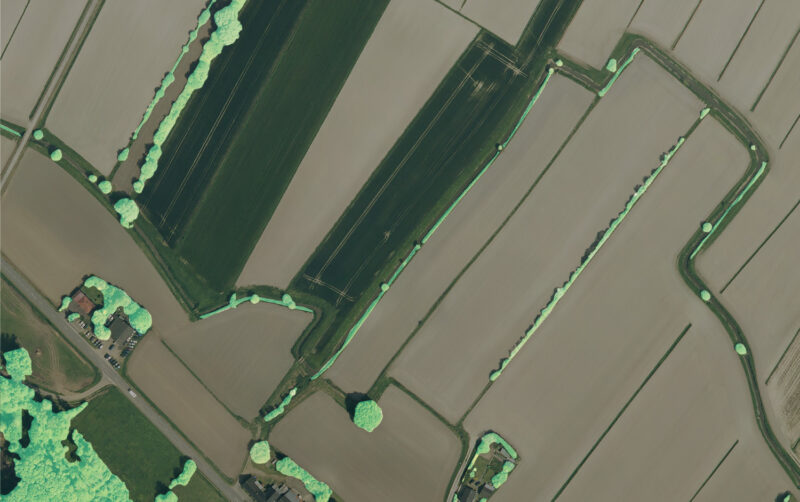
Earth observation for ecosystem conservation
Biodiversity indicators green infrastructure monitoring (bocage network inventory, hedge destruction and planting…)
03 Adaptation
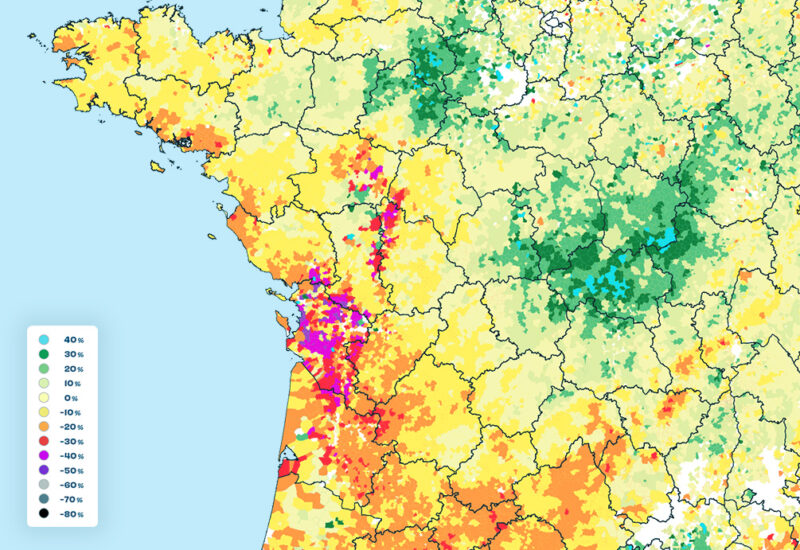
Quantifiying climate impact
Thanks to the analysis of optical and radar satellite imagery, get non-stop information on drought risks and farmland resilience
Forage production indicators
Identification of irrigated areas
Water stress indicators
Vegetation health indicators (NDVI, LAI…)

Your custom project & turnkey data
Kermap provides indicators tailored to your needs, using technical solutions designed for simplicity of access and operation : APIs, dashboards or deliverables. Contact us to learn more about our products for sustainable agriculture.
Automatized crop monitoring, field by field, at any scale
Kermap contributes to sustainable farming initiatives by providing crop analytics through satellite analysis. We combine expertise in remote sensing and artificial intelligence to deliver quick, large-scale multi-year crop identification. Our indicators and datavisualization tools provide actionable crop monitoring to anticipate on market trends, assess logistics needs, and certify the impact of environmental incentives for players involved in the transition to sustainable agriculture.
Crop identification from satellite imagery
Our innovative AI models enhance traditional crop identification using remote sensing, with gains in accuracy, velocity and scalability.
These deep learning techniques for instance proved successful in producing the first Europe and crop map in 2020 available on our demo platform, with the corresponding stats of production areas.
Crop identification for environmental services
You are a public actor, company, farm co-op, or non-profit organization involved in a greening or payment for ecosystemic services programme (PES) ? Our crop monitoring processes provide you with efficient tools and relevant indicators to support farming professionals towards the adoption or sustainable agriculture practices.
Crop analytics produced by Kermap support agroecology initiatives relying on soil conservation – such as EarthWorm Foundation’s participation au programme Sols Vivants Besides, Earth observation data can also contribute to water quality preservation, chemical input limitation or carbon sequestration.
Carbon offset for agriculture
Objective criteria to calculate carbon offset ? Through satellite data, crop analytics have some in store. We provide large-scale monitoring of farming practices fostering soil carbon storage, through the identification of crop rotation or cover crops among others.
These indicators produced by remote-sensing supply key contributions to carbon offset measurement. Players active in the carbon credit field can thus improve the reliability of their initiatives to encourage the reduction of CO2 emissions.















